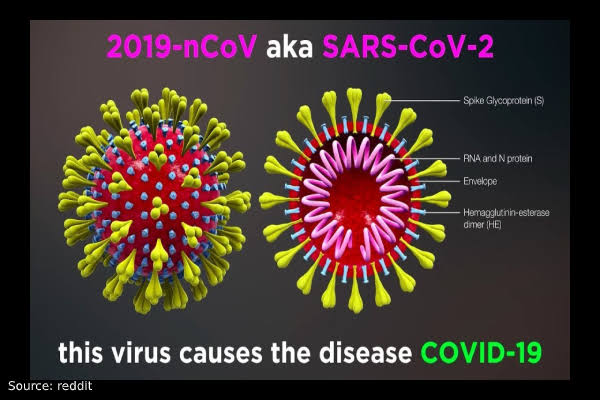
The new Corona virus, which is called “COVID-19” is a new type of corona virus that infects the human respiratory system and causes the emergence of respiratory diseases, and this virus first appeared in the Chinese city of Wuhan.
Corona viruses are a group of common viruses, and were named by this name because of the presence of some protrusions on their surface that resemble a “crown”, hence the name “CORONA”. Some of these viruses affect only animals, while some types of Corona virus can infect humans, causing symptoms similar to those of colds and influenza, which are mild to severe, and can also cause more serious diseases such as pneumonia and infections. airways; The types of corona viruses include the Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome virus (SARS), and finally the emerging corona virus (COVID-19).
And the Corona virus can be transmitted from one person to another, through droplets, when a person infected with the virus sneezes in front of a healthy person, as the virus can be transmitted if you are close to the infected person. The emerging corona virus can also be transmitted to humans by human contact with any surface with the virus on it and then touching the mouth or nose, but this is not believed to be the main way for the virus to spread.
The emerging corona virus causes respiratory diseases that range from mild to severe and may even lead to death in some cases, and symptoms usually begin to appear within two to 14 days of infection with the virus, and these symptoms include:
- fever.
- coughing;
- hard breathing.
How does the emerging corona virus infection spread?
The new Corona virus usually spreads from an infected person to another healthy person through one of the following ways:
- air, by coughing and sneezing.
- Direct contact with the infected person by touching or shaking hands.
- Touching an object or surface that has the virus, then touching your mouth, nose, or eyes before washing your hands.
- It is rarely transmitted through feces.
Who are the people most vulnerable to infection with the emerging corona virus?
Anyone can get infected with the emerging corona virus, but the people most susceptible to infection are children, the elderly, and people with a weak immune system or those with some chronic diseases such as kidney and liver disease and diabetes.
What are the symptoms of corona virus infection?
Symptoms depend on the type of coronavirus and how severe it is. If you have a mild to moderate upper respiratory infection such as the common cold, your symptoms may include:
- Runny nose.
- headache;
- coughing;
- sore throat.
- fever.
- Feeling of general tiredness and exhaustion.
Some coronaviruses can cause more severe symptoms and infections may turn into bronchitis or pneumonia, which symptoms include:
- Fever, which may be very high (more than 39 degrees Celsius).
- Cough with mucus.
- severe shortness of breath;
- Chest pain or shortness of breath and coughing.
Acute infections often occur in people with chronic heart disease or lung disease, people with weakened immune systems, infants, or the elderly.
Is there an effective treatment for the emerging corona virus infection?
So far, there are no specific treatments for the emerging corona virus infection, as health experts and the World Health Organization indicate that most cases will improve on their own. People infected with the emerging coronavirus can take some methods to relieve symptoms, and these methods include the following:
- Take over-the-counter pain medications to reduce pain, fever and cough, such as paracetamol and ibuprofen.
- Use a room humidifier or take a hot shower to help relieve a sore throat and cough.
- Get plenty of rest.
- Drink fluids so that the body does not become dehydrated.
Can corona virus infection be prevented?
At the present time, there are no vaccines to prevent infection with the emerging corona virus, but you can take some steps that help reduce the risk of infection and limit the spread of infection:
- Wash your hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds at a time, and if soap and water are not available, you can use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Avoid touching your nose, face, or mouth if you haven’t washed your hands.
- Avoid contact with a person who is infected with the Corona virus.
- Clean the surfaces you touch frequently.
- If you are coughing or sneezing, always cover your face with a tissue.
The new Corona virus is one of the Corona viruses that began to appear recently in China, specifically in the city of Wuhan, and then began to spread in many countries and countries around the world. Although there have been deaths due to the emerging corona virus, it is not considered a fatal epidemic so far, as the World Health Organization indicates that the death rate does not exceed 2% of infected cases, but it is considered an emergency situation of concern around the world. Avoiding contact with people infected with the Corona virus and maintaining your personal hygiene routine will help reduce the risk of infection significantly.