creatine; It consists of a combination of the amino arginine and methionine People often think of creatine as a steroid derivative, but creatine is not a steroid derivative but a combination of amino acids. If you are wondering what is creatine and what are the benefits of creatine , continue reading our article!

What is creatine?

It is transported to the brain and other tissues, and in these tissues, it turns into creatine phosphate, which is the energy storage form, by helping to break down ATP in sudden energy needs. As a high-energy phosphate compound that provides conversion, 95% of creatine is stored in the muscles, while as little as 5% is found in other tissues as creatine. After creatine phosphate is broken down, creatine is formed and the amount of creatine is produced depending on the individual’s body weight and muscle mass. Therefore, the blood level in men is higher than in women and children. After creatine phosphate is broken down, creatine is formed and the amount of creatine is produced depending on the individual’s body weight and muscle mass. Therefore, the blood level in men is higher than in women and children. After creatine phosphate is broken down, creatine is formed and the amount of creatine is produced depending on the individual’s body weight and muscle mass. Therefore, the blood level in men is higher than in women and children.
Energy metabolism and creatine relationship
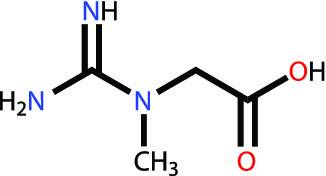
All living beings, including humans, need energy to survive. The immediate energy source for all cells is met by adenosine triphosphate, known as ATP. The short-term energy source for muscle contraction is ATP. During muscle contraction, ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP, or adenosine diphosphate, and this continues. With the sudden increase in energy requirement, a reaction occurs, which is catalyzed by the enzyme creatine kinase and formed by the breakdown of phosphocreatine, where phosphate and ADP combine to form ATP. As a result of this reaction, free creatinine accumulation occurs in the muscle. This accumulated creatine recombines with phosphate upon recovery to form phosphocreatine. The amount of phosphocreatine in muscle is 3 to 4 times the amount of ATP. The reason why the amount of creatine is higher than ATP in muscle is that the job of phosphocreatine is to provide energy for the replenishment of ATP. With a high intensity exercise, the amount of ATP is depleted in the first 3 seconds. The main reason for the formation of muscle fatigue is the decrease in the intracellular ATP concentration. Therefore, in order to delay muscle fatigue, the rate of regeneration of ATP should be close to the rate of hydrolysis. As a result, it is necessary to keep the creatine content of the muscle at an optimal level in order to provide high phosphocreatine stores. Therefore, in order to delay muscle fatigue, the rate of regeneration of ATP should be close to the rate of hydrolysis. As a result, it is necessary to keep the creatine content of the muscle at an optimal level in order to provide high phosphocreatine stores. Therefore, in order to delay muscle fatigue, the rate of regeneration of ATP should be close to the rate of hydrolysis. As a result, it is necessary to keep the creatine content of the muscle at an optimal level in order to provide high phosphocreatine stores.
What does creatine do?

The main function of creatine is to prevent age-related muscle loss. In studies, an increase in muscle strength has been observed in adult elderly people who do resistance training using creatine. Apart from this, creatine takes part in many mechanisms and contributes to the body. We have listed the benefits of creatine in the following articles.
Creatine helps improve athletic performance.

Creatine was first discovered in 1832, and creatine supplementation gained popularity after the 1992 Olympic Games in Barcelona. Today, creatine is widely used among professional athletes and bodybuilders to gain muscle, strengthen and improve exercise performance. Factors such as the type, intensity and duration of the exercise are related to the nutrition of the athlete. The 2 energy systems used according to the intensity of the exercise are anaerobic and aerobic energy systems. In short-term (less than 2 minutes) and high-intensity exercises, not all of the oxygen needed for energy production can be provided and oxygen deficiency occurs. In this oxygen deficient state, most of the required energy is provided by the ATP and phosphocreatine system. With creatine supplementation, creatine phosphate stores are supported, thus increasing the amount of ATP by helping creatine produce a high-energy molecule called ATP in the body. As a result, the increased amount of ATP helps to perform better during exercise. In addition to the energy consumption in exercises, another cause of fatigue is the accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles. Creatine acts as a buffer against this accumulation, making it easier for the muscles to work. It is known that creatine contributes to the increase of performance, especially in high-intensity efforts made for less than 2 minutes. Studies support this, and creatine supplementation has been found to increase strength and efficiency as well as lean body mass during short-term, high-intensity exercise. As a result, the increased amount of ATP helps to perform better during exercise. In addition to the energy consumption in exercises, another cause of fatigue is the accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles. Creatine acts as a buffer against this accumulation, making it easier for the muscles to work. It is known that creatine contributes to the increase of performance, especially in high-intensity efforts made for less than 2 minutes. Studies support this, and creatine supplementation has been found to increase strength and efficiency as well as lean body mass during short-term, high-intensity exercise. As a result, the increased amount of ATP helps to perform better during exercise. In addition to the energy consumption in exercises, another cause of fatigue is the accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles. Creatine acts as a buffer against this accumulation, making it easier for the muscles to work. It is known that creatine contributes to the increase of performance, especially in high-intensity efforts made for less than 2 minutes. Studies support this, and creatine supplementation has been found to increase strength and efficiency as well as lean body mass during short-term, high-intensity exercise. facilitates the work of the muscles. It is known that creatine contributes to the increase of performance, especially in high-intensity efforts made for less than 2 minutes. Studies support this, and creatine supplementation has been found to increase strength and efficiency as well as lean body mass during short-term, high-intensity exercise.
Increases muscle mass.

Creatine reduces muscle wasting and increases muscle strength. This increase in muscle mass is due to creatine retaining water along with it. With the increase in muscle mass and strength, it can be said that athletes using creatine supplements can train more intensely and for longer. At the same time, creatine reduces age-related muscle wasting and is protective against sarcopenia.
Reduces damage after injury.

Creatine reduces muscle cramps after intense resistance training thanks to its antioxidant effect. It is also known to accelerate the healing process in brain and other injuries.
Improves brain performance.

Studies have shown that creatine supplementation improves cognitive performance. It is useful in Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s, epilepsy, brain and spinal cord injuries.
In addition, studies have shown that creatine is effective in preventing skin aging, improving bone health, protecting against diabetes, protecting heart health, and preventing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. In addition, it is known that increased creatine consumption during pregnancy increases infant health.
What are the types of creatine?

Creatine Monohydrate
The most common supplement form of creatine is creatine monohydrate and is commonly used in sports drinks. Creatine monohydrate, which is easy to digest, safe, effective and more affordable, can be found in different forms such as powder, capsule, gel, candy. Creatine monohydrate consists of a creatine molecule and a water molecule. Approximately 90% of the creatine monohydrate form is creatine and 10% is water. Creatine monohydrate binds water before it enters the muscle cells and thus can also increase the water content in the muscle cells. This can promote muscle growth. Although studies have not found a common side effect of creatine monohydrate, the generally seen minor side effect is stomach cramps. When minor side effects occur, typically stomach cramps or cramps occur. These side effects can be alleviated by consuming several small doses rather than one large dose.
Creatine Ethyl Ester
Creatine ethyl ester is considered superior to other types of creatine. Creatine ethyl ester has no side effects and is better absorbed from the stomach and muscles than creatine monohydrate. As a result of the absorption of creatine ethyl ester in the stomach, stomach problems are eliminated. The reason why creatine ethyl ester is better absorbed in the muscles than the monohydrate form is that it needs less water molecules outside the muscle.
Magnesium Creatine Chelate
Magnesium creatine chelate is a new form of creatine that has magnesium attached to creatine. When the studies done with magnesium creatine chelate are examined, it is seen that it has not been clarified yet. In an animal study, 2 groups using magnesium creatine chelate and monohydrate forms were compared and it was found that the physical performance of the group using magnesium creatine chelate was higher. In another study, improvement was observed in each of the performances of the creatine monohydrate and magnesium creatine chelate groups, but no big difference was found between them. As a result, it was concluded that magnesium creatine chelate is not better than monohydrate forms.
Creatine HCL
Creatine HCL is the newest form of creatine. It can be said that it is stronger than other types of creatine. Creatine HCL is water soluble and thus more easily absorbed into the bloodstream.
What should be considered when choosing creatine?

According to studies with creatine, the most effective and safe form is creatine monohydrate. There are more studies on creatine monohydrate, which is preferred because it is more affordable than other forms, and thus has more reliability than others.
What should the dose of creatine be?

Creatine is found in 450 grams of red meat, up to 2 grams. Information on the recommended dose of creatine varies. The daily creatine requirement of those who do bodybuilding sports can vary from 5 gr to 20 gr. Many athletes, on the other hand, need creatine supplementation because they cannot provide this amount with their natural diets. The amount that needs to be consumed for the supplement to be beneficial varies between 1-6 teaspoons, that is, 5-30 grams. It is recommended to take the supplements under the control of a doctor in order to be wary of excessive consumption. Most commercially available creatine supplements are packaged to contain 4 to 5 grams of creatine per dose. While some of these supplements recommend once-daily dosing, most seem deliberately vague about recommended dosing frequency or duration. These products, Not regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration. Therefore, these commercial products are often not entirely safe and may contain undesirable ingredients such as prohibited substances.

