Milk and permanent teeth suffer from several deformities, and these deformities may be in the number of teeth, their shape, color, or composition.
** Number distortions
There may be a deficiency in the number of teeth and incompleteness of the necessary number, and we may also see a space between the teeth that belongs to one or more teeth, and this is often the case in
People also experience an increase in the number of teeth, and their number becomes greater than the number of permanent teeth, such as the central incisor and the wisdom tooth, which begin to disappear often enough. This is when we see the presence of one or more teeth outside the range of the teeth, such that part or all of the crown of the tooth is changed, and this is because some teeth resemble the teeth of animals. They are cone-shaped, have cusps on the front teeth, or have an increase in the number of cusps on the back teeth.
** Color distortions
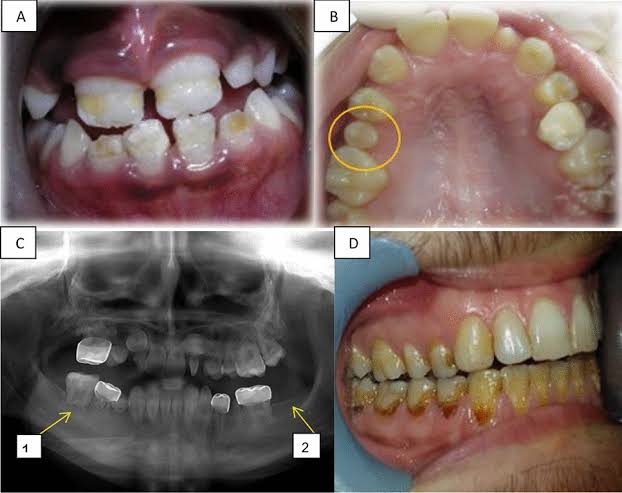
It is noted that some teeth are partially or completely stained and the stain cannot be removed by cleaning
– Bacterial dental plaque:
It is a thin, smooth, homogeneous layer consisting of many germs surrounded by an organic substance from saliva adhered to the outer surface. It is the main factor in the occurrence of tooth decay. If it is left for a long time without removing it, it hardens in the form of calcareous deposits of a light brown color and in turn affects the tissues. Bonding to the tooth, and then helps the tooth become loose and then fall out.
** tooth decay :
Diseases that affect the mouth have increased. Once a child reaches the age of five, we see approximately 4 teeth affected by decay, and more than 10 teeth affected by decay in adulthood. It is known that tooth decay occurs as a result of neglect and lack of care for oral and dental hygiene. Generally, tooth decay occurs if carbohydrates (sugars + starches), bacteria, and time combine. Caries occurs anywhere in the tooth and is common in places that are difficult to clean. Complications of cavities include tooth erosion, tooth extraction, and abscesses under the roots.
** Teeth staining:
Some teeth are partially or completely stained, and this staining can be external (on the surface of the crown), or internal (inside the pulp). Teeth are usually colored yellow, dark green, or grey.
– External staining: Smoking or neglecting to brush the teeth stains the teeth in a gray color, which is abundant in the front teeth. Failure to remove calcareous materials also turns them yellow.
A- Internal coloring: Teeth may be colored and it is difficult to remove that color using the usual methods. This comes from several factors:
– Through the blood: During the stages of tooth formation, the infant may be infected with some diseases, and stains may occur through the blood circulation heading to the vessels of the pulp: such as typhoid fever, cholera, liver infections, and heart and blood diseases.
– By losing the vitality of the tooth: such as being injured by a punch, or breaking part of the tooth as a result of taking medications: such as tetracycline antibiotics.
** Impacted teeth
These are teeth that were prevented from erupting for various reasons and remained covered by the jawbone after the time of their eruption. This is either due to delayed loss of the temporary tooth, or early loss of it, or lack of jaw growth, or the presence of infections, or the abnormal position of adjacent teeth, and perhaps genetics, or anemia, rickets, or endocrine disorders.
– Complications:
Infections, fractures, pain…
Sometimes it hinders the orthodontic process, causes decay in adjacent teeth, and pushes adjacent teeth away from the occlusal plane.