Pancreas cancer
Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer
Cancer that originates in the pancreas is divided into two types: pancreatic ductal cancers (called adenocarcinomas)
In more than 90% of cases, the remaining cancers are tumors of cells (often insulin-producing cells) that make hormones.
Pancreatic cancer almost always affects the elderly, and the incidence of this disease increases as age increases and lifespan increases.
Cigarette smoking and chronic pancreatitis may be contributing factors.
Symptoms:
When pancreatic cancer arises, the only symptom is often a non-specific feeling of discomfort in the abdomen. Another symptom is pain.
It hurts the abdomen, radiates from the abdomen to the back, and improves whenever the patient bends his body forward. The patient’s appetite also weakens and his weight decreases.
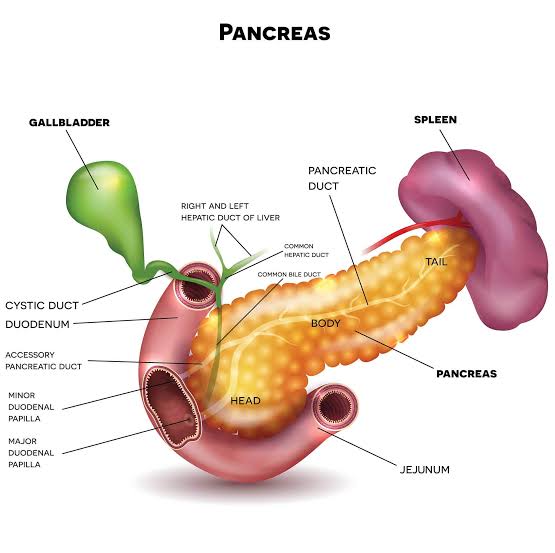
Most pancreatic tumors affect the head of the pancreas. When these tumors grow larger, they can block the passage of bile from the liver
It blocks the bile ducts heading to the intestines, making bilirubin (a yellow-orange bile pigment)
It accumulates in the body, followed by the appearance of jaundice and itching, and the color of urine is brown and the color of stool is very light, the color of clay, at a time when
Jaundice appears, and the tumor has often grown significantly in size.
In the case of tumors that consist of hormone-producing cells, the symptoms depend on the hormone that is produced in large quantities.
In most of these cases, this hormone is insulin, which leads to a decrease in its production
Blood sugar levels and a tendency to faint, disorientate, tremble, and sweat.
Pancreatic cancer treatment options:
If the doctor suspects the presence of pancreatic cancer, he will conduct a number of tests or examinations, including blood tests for detection
About tumor markers (which are proteins produced by tumors that circulate in the bloodstream ).
Although ultrasound and computer tomography are the mainstay of identification
Pancreatic cancer and determining the extent of the tumor’s progress, both methods can miss the diagnosis of some cancer cases.
Other tests include endoscopy to visualize the bile ducts and pancreas with retrograde injection, which
It also allows a sample of the tumor to be taken for examination and to remove any blockage.
Doctors sometimes use a computerized tomography scan to guide a fine needle until it reaches the pancreas
To collect some cells that are examined under a microscope to determine whether they are cancerous or not.
The only treatment for pancreatic cancer is to remove all or part of the pancreas, which is only effective in the few patients who…
Their cases were diagnosed before the cancer had spread, the possibility of relapse is high, and it is more likely if cancer cells are found in the nodes
Nearby lymph nodes or if the tumor has spread to nearby tissues.
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy may be used to shrink tumors or treat them after resection surgery, but these treatments do not prolong life.