Lupus erythematosus or systemic lupus erythematosus, also known as lupus, is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body.
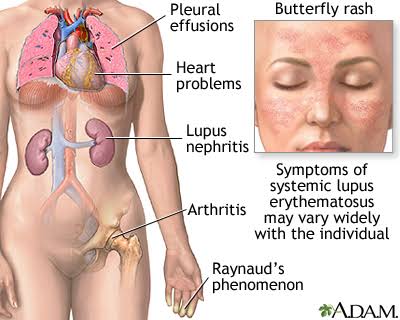
Symptoms vary between people and can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms include arthritis, fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, and a red rash on the face is the most common symptom.
The cause of this disease is not entirely clear. It is believed to involve hormonal, environmental and genetic factors. The evidence for this is found among identical twins, if one of them is affected, there is a 24% chance that the other will be affected by sunlight, vitamin D deficiency, and some injuries, increasing the risk of developing the disease.
The mechanism involves: an immune response to antibodies against a person’s own tissues. This is the main cause of disease, as the antibodies attack the normal living tissues of the body itself, causing these infections in different parts of the body.
Diagnosing such a condition is not easy as it is based on a combination of symptoms and laboratory tests. There are other types of lupus erythematosus including discoid lupus erythematosus, neonatal lupus, and cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
There is no cure for lupus erythematosus, and treatments may include an anti-inflammatory. It has not been shown that alternative medicine has added a cure for this disease. SLE significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and this is the most common cause of death.
With modern treatment about 80% of those affected survive more than 15 years. Women with lupus have more high-risk pregnancies but are often successful.
Disease rates between countries range from 20 to 70 per 100,000 population. Women of childbearing age are affected about nine times more often than men. While the most onset of the disease begins between the ages of 15 and 45, therefore, a wide range of ages can be affected. People of African, Caribbean and Chinese descent are at greater risk than whites. Disease rates in the developing world are unclear.
lupus erythematosus symptoms
The disease negatively affects several organs in the body, and accordingly, the symptoms differ according to the affected system. It should be noted that the disease has periods of activity during which symptoms appear clear and others of latency in which the disease subsides.
Predominant symptoms:
Feeling sick and tired
High temperature
Anorexia
Joint and muscle pain
mouth ulcers
Redness in the face, takes the shape of a butterfly
Excessive sensitivity to light
Infections of the lining of the heart and lungs
It is not necessary for all of these symptoms to occur, as the severity of the disease and the extent of the body’s impact varies from one person to another. Symptoms may appear in the form of chronic heat of unknown cause or periods of joint and muscle pain. The most important organs in our bodies and the most dangerous if the disease reaches them are the brain, liver and kidneys. Leucopenia also often causes a deficiency in all blood cells, which leads to an increased risk of infections.