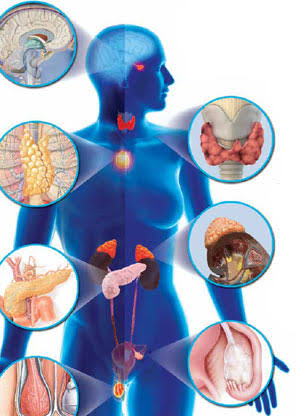
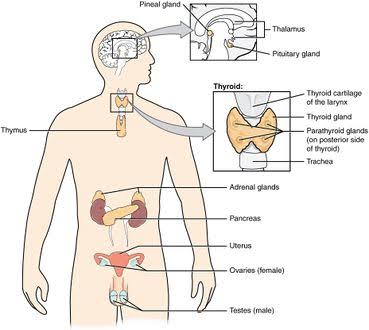
Endocrine disorder is a pathological condition caused by the over or underproduction of hormones from the endocrine glands (the glands that secrete their hormones directly into the blood) such as the pancreas, pituitary gland, thyroid and adrenal glands. Examples of endocrine disorders include diabetes mellitus, acromegaly, Graves’ disease, Addison’s disease, hyper and hypothyroidism, Cushing’s syndrome, and other disorders.
Endocrine disorders causes
There are many factors that cause endocrine disorders, and they often result from impaired function of the pancreas, pituitary gland, thyroid gland or adrenal gland. Some factors also increase the chance of endocrine disorders, including: – Family history of endocrine disorders. High blood cholesterol. – Malnutrition . Pregnancy. History of autoimmune disorders such as diabetes. Decreased physical activity.
Endocrine disorder symptoms
Symptoms of endocrine disorders vary from moderate to chronic and depend on the affected organ.
Endocrine disorder treatment
Endocrine disorders treatment may include pharmaceutical drugs (manufactured hormones) to achieve hormonal balance in addition to surgical or radiological intervention in disorders caused by abnormal tissue growth in one of the endocrine glands.
How can endocrine disorder be prevented?
Although many endocrine disorders are linked to genetic factors, lifestyle may play a role in increasing the chance of infection, which calls for adherence to the following preventive measures: – Adherence to a healthy and balanced diet. Doing exercise regularly. – Avoid smoking.
Endocrine disorder complications
The complications associated with endocrine disorders vary in severity and are as follows: – Anxiety and insomnia (thyroid disorders). – coma. – Depression . Heart disease. Nerve damage. Organic damage or failure. Poor quality of life.