Why do you need to create a plan for a healthy eating pattern?
Diabetes diets
If you have diabetes or prediabetes, your doctor will often recommend that you see a dietitian to help you plan a healthy eating pattern. The plan helps you control your blood sugar (glucose), control your weight and control heart disease risk factors, such as high blood pressure and high blood fats.

When you overeat calories and fat, your body creates an unwanted spike in blood glucose. And if your glucose isn’t constantly checked, this can lead to serious problems, such as a high blood glucose level (hyperglycemia) and, if elevated, can lead to long-term complications, including nerve, liver and heart atrophy.
You can help keep your blood glucose levels in a safe range by making healthy food choices and monitoring your eating habits.
For most people with type 2 diabetes, losing weight can facilitate blood glucose control and provide a host of other health benefits. If you need to lose weight, a diabetes diet provides a structured and nutritious way to reach your goal safely.
What does a diabetes diet involve?
The diabetes diet is based on eating three meals at regular times during the day. This system helps the body make better use of the insulin it produces or obtains through drug absorption.
A registered dietitian can help you design a diet based on your health goals, desires, and lifestyle. Your dietitian can also discuss with you how to improve your eating habits, such as choosing portion sizes to suit your needs and based on your size and activity level.
Recommended foods
Block your calorie count with these nutritious foods. Choose healthy carbohydrates, high-fiber foods, fish and “good” fats.
healthy carbohydrates
During digestion, sugars (simple carbohydrates) and starches (complex carbohydrates) are broken down into glucose in the blood. Focus on healthy carbohydrates, such as:
the fruit
vegetables
Whole grains
Legumes such as beans and peas
Low-fat dairy products, such as milk and cheese
Avoid less healthy carbohydrates, such as foods or drinks that contain added fats, sugars and sodium.
High-fiber foods
Dietary fiber includes all parts of plant foods that the body cannot digest or absorb. Fiber eases the way your body digests and helps control blood sugar levels. Foods rich in fiber include:
vegetables
the fruit
nuts
Legumes such as beans and peas
Whole grains
Heart-healthy fish
Eat heart-healthy fish at least twice a week. Fish, such as salmon, mackerel, tuna and sardines, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which may prevent heart disease.
Avoid fried fish and fish that contain high levels of mercury, such as king mackerel.
“good” fats
Foods containing monounsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats can help lower blood cholesterol levels. They include:
avocado
nuts
Olive, canola, and peanut oils
But do not overdo it; As all fats are rich in calories.
Foods to avoid
Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease and stroke by accelerating the growth of clogged, hardened arteries. Foods containing the following can harm your goal of a heart-healthy diet.
Saturated fat. Avoid fatty dairy products and animal proteins, such as butter, beef, sausage, sausage and bacon. Also reduce your intake of coconut and palm kernel oils.
Trans fats. Avoid trans fats found in ready-made snacks, baked goods, butter and margarine.
cholesterol. Sources of cholesterol include fatty dairy products, animal proteins, egg yolks, liver and other meats. Have no more than 200 mg of cholesterol per day.
Sodium. Have no more than 2,300 mg of sodium per day. Your doctor may suggest eating less if you have high blood pressure.
Conclusion Make a plan
You can use a few different methods to create a diabetes diet; To help you keep your blood sugar level within the normal range. With the help of a nutritionist, you may find that one or a combination of the following methods works for you:
Dish method
The American Diabetes Association offers a simple way to plan meals. In essence, it focuses on eating more vegetables. Follow these steps when preparing your dish:
Fill half of your plate with non-starchy vegetables like spinach, carrots, and tomatoes
Fill a quarter of your plate with protein, such as tuna, lean meat or chicken.
Fill the last quarter of the plate with a whole grain nutrient or a starchy vegetable such as green peas.
And you should include “good” fats such as nuts or avocados in small quantities.
Add a serving of fruit, dairy, tea or coffee without sweetener.
carbohydrate counting;
Because carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, they have a big impact on your blood glucose levels. To help control your blood sugar level, you may need to learn how to calculate the amount of carbohydrates you eat so that you can adjust your insulin dose accordingly. It is necessary to track and count the amount of carbohydrates in each meal or snack.
A dietitian can teach you how to calculate portions of food and how to read food labels in an educated way. It can also: Teach you how to pay special attention to portion size and carbohydrate content.
If you take insulin, a dietitian can teach you how to count the amount of carbohydrates in each meal or snack and adjust your insulin dose accordingly.
Choose your foods
Dietitians may recommend that you choose specific foods to help you plan your meals and snacks. You can choose a number of foods from lists that include categories such as carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
One portion of food in each category is known as a “choice.” One food choice has the same amount of carbohydrates, protein, fat, and calories—and the same effect on your blood glucose—as a serving of every other food in the same category. For example, a list of starches, fruits and milk includes options with 12 to 15 grams of carbohydrates.
glycemic index
Some people with diabetes use the glycemic index; To choose foods, especially carbohydrates. This method ranks carbohydrate-containing foods based on their effect on blood sugar levels. Talk with a dietitian about whether this method might work for you.
sample menu
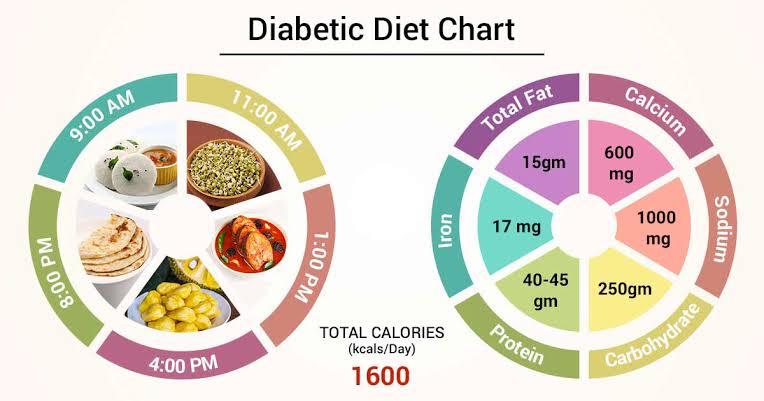
When planning meals, consider size and activity level. The following list is designed for a person who needs 1,200 to 1,600 calories per day.
the breakfast. Whole wheat bread (1 medium slice) with 2 teaspoons jelly, 1/2 cup shredded wheat cereal with 1 cup low-fat 1 percent milk, a piece of fruit and coffee
the lunch. Grilled beef sandwich on wheat bun with lettuce, low-fat American cheese, tomato, mayonnaise, medium apple and water.
dinner. Salmon, 1 1/2 teaspoons vegetable oil, small baked potatoes, 1/2 cup carrots, 1/2 cup green beans, medium white dinner roll, unsweetened iced tea, milk.
Snack. Two and a half cups of popcorn with one and a half teaspoons of ghee
What are the results of following a diabetes diet?
Sticking to a healthy eating plan is the best way to keep your blood glucose under control and prevent complications from diabetes. And if you need to lose weight, you can adjust this diet to suit your specific goals.
Besides controlling diabetes, the diabetes diet offers other advantages as well. Since the diabetes diet recommends eating plenty of fruits, vegetables and fiber, its use is likely to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and certain types of cancer. Eating low-fat dairy products may also reduce your risk of low bone mass in the future.
Are there any risks?
If you have diabetes, it’s important to work with your doctor and dietitian to develop a nutritional plan that works for you. You should also eat healthy foods, and keep portions in check to control your blood glucose levels. Not sticking to the prescribed diet puts you at risk of fluctuating blood sugar levels and other more serious complications.