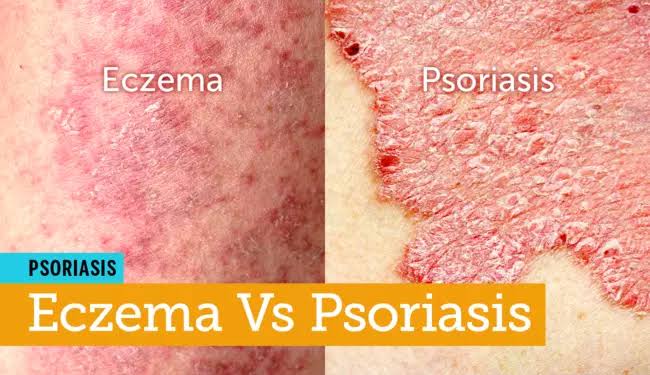
Psoriasis is a skin disorder that causes skin cells to multiply 10 times faster than normal, causing the skin to build up in red patches covered with white scales that grow anywhere, but most appear on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back.
Psoriasis usually appears at the beginning of puberty, and for most patients it affects only a few areas, and in severe cases psoriasis can cover large parts of the body, and the spots can heal and then return again during the patient’s life, knowing that it is not an infectious disease and is not transmitted from a person etc.
Psoriasis occurs when skin cells are replaced more quickly than usual. So far, the causes of psoriasis are still unknown, but research suggests that it is caused by a problem with the immune system.
Factors that increase the chances of developing psoriasis
World Psoriasis Day is celebrated on October 29 every year. To raise awareness of the disease and ways to deal with and support patients with psoriasis, studies have confirmed that 15% of people with psoriasis show signs of depression, and up to 48% suffer from anxiety disorders.
1- Immune system disorder
The immune system is the body’s defense against disease and helps fight infection. One of the main types of cells the immune system uses are called T cells. These cells normally travel through the body to detect and fight invading germs, such as bacteria, but people with psoriasis struggle to attack the skin cells. By chance, this causes new skin cells to be produced in the deepest layer of the skin more quickly than usual, and stimulates the immune system to produce more T cells.
The exact cause of this problem with the immune system is unknown, although certain genes and environmental triggers may play a role.
See also: Turmeric treats cancerous tumors
2- heredity
Psoriasis runs in families, so you may be more likely to develop psoriasis if you have a relative with the condition, but the exact role genes play in psoriasis is unclear, as research has shown that many different genes are linked to the development of psoriasis, and it is possible that different combinations of genes They may make people more likely to develop this condition, but having these genes does not necessarily mean that you will develop psoriasis.
Causes of psoriasis
For many people, psoriasis symptoms start or get worse because of a specific event called a trigger. Common psoriasis include:
Skin injury such as a cut, scrape, insect bite, or sunburn Smoking stress Hormonal changes especially in women during puberty and menopause Certain medications – such as lithium, some antimalarials, anti-inflammatory drugs including ibuprofen, and ACE inhibitors ( Throat infections: Some people, especially children and young adults, develop a form of psoriasis called “intestinal psoriasis” after a streptococcal throat infection, but most people with strep throat do not develop psoriasis. Other immune disorders such as HIV human immunity