The majority of nutritional professionals agree that saturated fat is not particularly healthy and should be consumed in only limited diets. Most studies have routinely shown that diets high in saturated fat intake increase the risk of high cholesterol, atherosclerosis, heart disease, stroke. In fact, saturated fat and trans fats are actually more responsible for increasing levels of low-density lipoproteins (LDL) cholesterol, commonly referred to as “ bad” cholesterol, than consuming foods high in cholesterol itself. That said, there seems to be an exception to the rule — coconut oil.
Coconut oil is extremely high in saturated fat, yet unlike animal sources of saturated fat, there is a rather expansive body of evidence demonstrating quite a few health benefits of this plant- based saturated fat. Accordingly, coconut oil has earned superfood status in many health and wellness circles and is used as both a nutritious and flavorful fat in both sweet and savory vegan and paleo dishes and consumed as is, right off the spoon, by many people looking to capitalize on its reported health benefits. Whether you follow a paleo, keto, vegan diet, or low-carb diet and have already jumped on the coconut oil bandwagon or want to understand why coconut oil is touted as a healthy elixir, keep reading for a list of the health benefits of coconut oil.
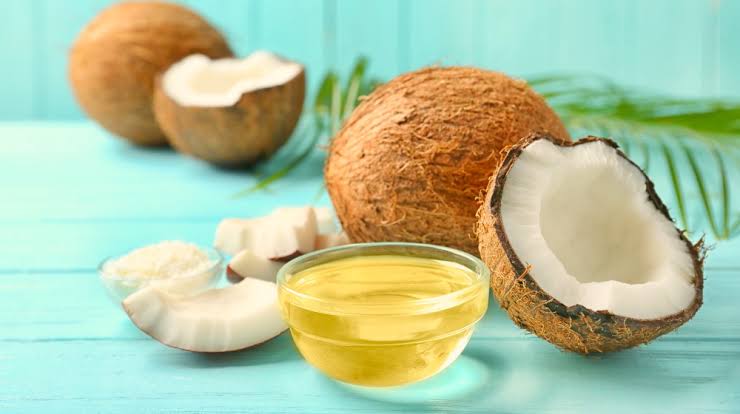
What Is Coconut Oil?
Coconut oil is a fat that is made by pressing coconut meat and concentrating the oils. Because coconut oil is 80% to 90% saturated fat, it is solid at room temperature but has a relatively low melting point. There are different types of saturated fats in coconut oil, but about 51% of the saturated fat is lauric acid, which is considered a medium-chain triglyceride because it has 12 carbons in the fatty acid chain.
Benefits of Coconut Oil
The health benefits of coconut oil are mainly attributed to the medium-chain triglycerides as well as some of the unique phytonutrients and antioxidant properties of coconut.
Coconut Oil Has Antibacterial Properties
Coconut oil can support your immune system and the beneficial bacteria in your gut and mouth by preferentially killing harmful pathogenic bacteria and fungi while preserving desired species. For example, the lauric acid in coconut oil has antimicrobial and antibacterial properties and has been shown to be effective against Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus mutans, Escherichia coli, and Helicobacter pylori, among others.
Coconut Oil May Increase Fat Burning
Coconut oil is a rich source of medium-chain triglycerides, which have been shown to boost metabolic rate and help mobilize fatty acids to energy production. Studies investigating the effects of supplementing with medium-chain triglycerides have demonstrated that these saturated fats can enhance weight loss.
Coconut Oil May Support Athletic Performance
About 65% of the fat in coconut oil is comprised of medium-chain triglycerides. Unlike other fats, these fatty acids are digested and absorbed rapidly, providing a quick boost of energy. Studies have shown that medium-chain triglycerides are as effective at quickly fueling working muscles and supporting energy production as carbohydrates, which are generally considered to be the preferred fuel of working muscles.
Coconut Oil May Curb Appetite
One of the reported benefits of the paleo diet and keto diet is that adherents report feeling less hungry. This appetite-modulating effect of high- fat, low-carb diets is attributed to the ketones produced when fats are metabolized in the absence of carbohydrates. Ketones seem to suppress some of the hormones involved in regulating hunger signals, so you may feel less hungry. Moreover, fats are filling because they contain nine calories per gram and take longer to break down than carbohydrates. As such, it’s possible you may eat less if you start incorporating coconut oil into your diet, depending on your energy needs and overall diet composition.
Coconut Oil Can Hydrate and Nourish Your Skin
The fats, oils, and vitamin E in coconut oil help hydrate skin cells, preventing dry skin and nourishing cell membranes in skin cells to optimize the texture and appearance of skin and prevent dullness and sagging. Furthermore, research has demonstrated the effectiveness of coconut oil in combating inflammatory skin conditions like atopic dermatitis by supporting skin barrier function by preventing excess water loss and minimizing the irritating effect of allergens and infectious agents.
Coconut Oil Can Strengthen Your Hair
If you are frustrated with split ends or thinning hair, here’s another reason to consider coconut oil: Just as the fats and vitamin E in coconut oil can nourish your skin cells, so too do these nutrients support the health of your hair follicles and even hair strands. A study demonstrated that coconut oil is able to penetrate deep into hair strands—into the core—and make the hair more flexible and able to withstand tension without breaking.
Coconut Oil Can Fight Bad Breath, Plaque Buildup, and Gingivitis
If you’ve heard of oil pulling, you’re probably familiar with the oral hygienic effects of coconut oil. In much of the same way as a conventional antiseptic mouthwash cleans your mouth to kill disease- and plaque-forming bacteria, swishing with coconut oil (a process called oil pulling), has been found to reduce bad breath, kill pathogenic species, and support oral health and hygiene as effectively as antiseptic mouthwashes. Plus, the lauric acid in coconut oil can protect against plaque buildup, gum inflammation, and cavities.
Coconut Oil Supports Brain Health
The medium-chain triglycerides in coconut oil have been linked to reducing the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, and other age- related declines in cognitive performance by providing the brain with an alternative fuel source to glucose in the form of ketones. Coconut oil has even been shown to reduce the incidence of seizures in those with epilepsy.
Coconut Oil May Reduce Cellular Damage and the Risk of Disease
Coconut is high in antioxidants such as tocopherols, tocotrienols, flavonoids, and polyphenols. Antioxidants are natural plant- based compounds that confer health benefits in the body by neutralizing harmful free radicals. Free radicals cause oxidative damage in the body, potentially altering DNA and turning on or off genes, and can cause premature cell death, cellular aging, inflammation, and cancer. Diets high in antioxidants can protect against this adverse cellular damage and the risk of certain inflammatory diseases and cancer.