What Is Crohn’s Disease? Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
What Is Crohn’s Disease? Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that affects the digestive tract. It can cause severe abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, and malnutrition. Living with Crohn’s can be challenging, but with proper management and medical care, many people lead full, active lives.
In this article, we’ll cover the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for Crohn’s disease. If you’re searching for answers or suspect you may have this condition, you’re in the right place.
What Causes Crohn’s Disease?
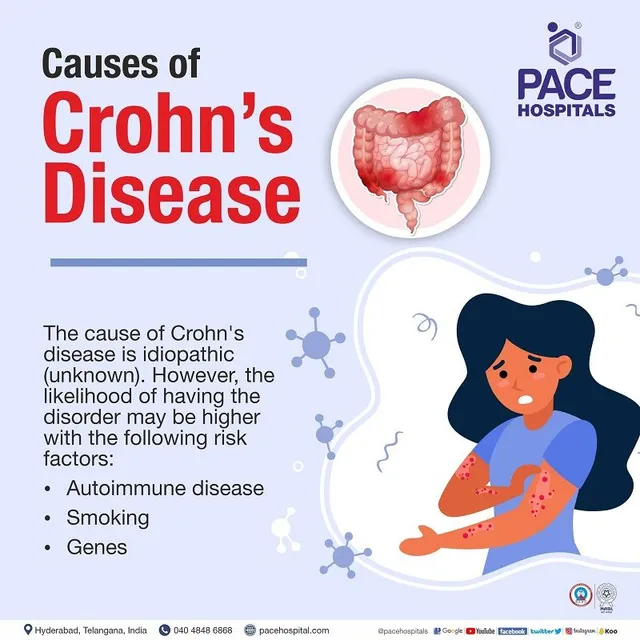
While the exact cause of Crohn’s disease is unknown, experts believe it results from a combination of:
-
Genetics: Family history increases your risk.
-
Immune system malfunction: The immune system attacks healthy gut bacteria.
-
Environmental factors: Smoking, diet, and stress can contribute to flare-ups.
-
Gut microbiome imbalances: Changes in intestinal bacteria may play a role.
Common Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease symptoms can range from mild to severe and may come and go over time. Common signs include:
-
Persistent diarrhea
-
Abdominal cramps and pain
-
Fatigue or low energy
-
Unintended weight loss
-
Blood in the stool
-
Mouth sores
-
Reduced appetite
-
Fever during flare-ups
Symptoms vary depending on where the inflammation occurs in the digestive tract. Some people may also experience joint pain, skin issues, or eye inflammation.
How Is Crohn’s Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Crohn’s disease typically involves several tests, including:
-
Blood tests (to detect inflammation or anemia)
-
Stool tests (to rule out infections)
-
Colonoscopy or endoscopy (to view inflammation)
-
Imaging tests (MRI, CT scans, or capsule endoscopy)
A gastroenterologist may also take a biopsy (a small tissue sample) during a colonoscopy to confirm the diagnosis.
Crohn’s Disease Treatment Options
While there’s no cure for Crohn’s disease, several treatments can help manage symptoms and reduce inflammation:
1. Medications
-
Anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., corticosteroids, mesalamine)
-
Immune system suppressors (e.g., azathioprine, biologics)
-
Antibiotics (for infections)
-
Antidiarrheal drugs and pain relievers
2. Diet and Nutrition
-
Work with a dietitian to identify trigger foods.
-
Eat smaller, more frequent meals.
-
Stay hydrated.
-
Consider a low-residue diet during flare-ups.
3. Surgery
If medications aren’t effective, surgery may be needed to remove damaged sections of the intestine or treat complications such as blockages or fistulas.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Crohn’s Disease
-
Quit smoking (it worsens symptoms)
-
Reduce stress through yoga, meditation, or exercise
-
Keep a symptom journal to track food triggers
-
Join a support group or talk to a counselor
-
Stay on top of medical appointments and lab work
When to See a Doctor
If you’re experiencing ongoing digestive issues or any of the symptoms listed above, consult a gastroenterologist. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve your quality of life.