Vitamin D
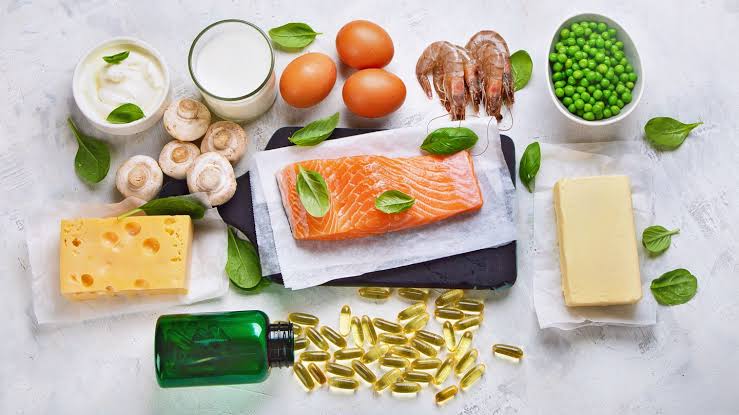
Vitamin D is considered a group of fat-soluble vitamins. This vitamin is found in small quantities in some foods, the most important of which are fatty fish such as sardines, tuna, and cod liver oil. Due to its scarcity in food, it has been manufactured and added to basic foodstuffs such as milk and juice to become fortified foods. With vitamin D, it is also found in the form of medicinal supplements such as intramuscular needles, drops, pills, and capsules taken orally. As for the main source of vitamin D, it is sunlight, so it is called the sunshine vitamin. Most of the vitamin D the body needs is obtained from it. From daily exposure to sunlight, the skin, with its special receptors, converts sunlight into vitamin D, which is then stored in fatty tissue in the human body.
The function of vitamin D is to control the level of calcium and phosphorus in the blood, as it enhances the ability of the bones to absorb calcium, thus ensuring the strength and density of the bones. As a result, those with a deficiency in the level of vitamin D suffer from symptoms related to the bones, the most important of which is rickets or rickets. Bones in children and osteoporosis in adults and the elderly, accompanied by a constant feeling of fatigue and exposure to bone fractures from time to time.
Vitamin D deficiency is widespread in people who are not exposed to the sun sufficiently, and it also affects the elderly who suffer from poor absorption, which affects the rate of absorption of vitamin D from the stomach to the blood. In contrast, infants who depend entirely on breast milk The mother has a vitamin D deficiency unless they are exposed to sunlight on a daily basis. We mention here that the treatment takes place in two stages: the compensatory stage, in which the patient is given high doses of vitamin D. After that, the level of the vitamin in the blood is evaluated so that the preventive stage comes during which The patient is given the daily doses recommended by health organizations in order to maintain the level of vitamin D within normal limits.
These doses may change depending on the health condition of the human body and the medications he is taking that may affect the level of vitamin D in the blood. It should be noted that one should not take the initiative to take any type of vitamin without consulting a doctor, especially vitamin D here, because taking This vitamin in doses larger than what the body needs leads to what is called hypervitamin D (hypervitaminosis D), which is extremely dangerous because the solubility of vitamin D in fat makes getting rid of it naturally not easy, so we, as a medical team, advise that Vitamin D should not be taken from pharmaceutical supplements without measuring its level in the blood first and consulting a specialist doctor second. As for the symptoms of excess and increased levels of Vitamin D, they are the accumulation of calcium in the blood, and these symptoms include vomiting, nausea, poor appetite, and a feeling of constant fatigue and exhaustion. …Also, some kidney functions may be affected as a result of an increase in the level of vitamin D in the blood.
Finally, we always repeat that prevention is better than cure, and continuous health follow-up protects against many unwanted symptoms resulting from a deficiency or excess of vitamin D in the body.