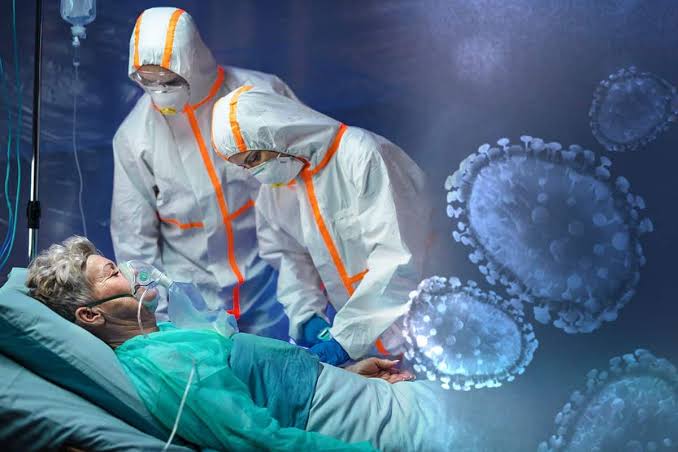
A recent study indicates that a type of fat reduces the risk of death from the emerging corona virus “Covid-19”, so what is it, and where is it located?
The study was conducted by researchers from the United States at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, and was published in the journal ” Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes & Essential Fatty Acids “.
And the fats that researchers found to reduce death with Covid-19 are “omega-3 fatty acids”, which are found in fish oil, salmon, herring, mackerel and sardines, and are also available in the form of nutritional supplements.
We emphasize here that the information that we will present here for guidance, as fish oil is not a treatment for Covid-19 and is not a substitute for disease prevention measures such as social distancing, wearing masks and personal hygiene. And you should also consult your doctor about how to get “omega-3”, does it suit your condition and can help you reduce the risk of complications from “Covid-19”?
The researchers measured the index of “omega-3” acids in the blood of 100 patients infected with the “Covid-19” virus, and the risk of death was analyzed, and the researchers found that a high level of “omega-3” acids may reduce the risk of death with Covid-19, by 75%. %.
The researchers said that the long-chain omega-3 fatty acids Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) have anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce morbidity and mortality rates from Covid-19 infection.
The researchers stated that severe and fatal “Covid-19” disease is caused, in part, by rapid elevations of inflammatory cytokines such as “TNF-alpha”, “interleukin-1 beta” (IL-1β) and “interleukin-6” ( IL-6), leading to cytokine release syndrome or “cytokine storm.” According to this, one of the preventive methods for “Covid-19” infection is to reduce cytokine release.
In a cytokine storm, a dangerous immune response occurs, as immune cells are overproduced and enter the lungs, leading to a deterioration in the body similar to septicemia. This is accompanied by a decline in the ability to breathe and pneumonia, which can eventually lead to death.
cytokine
The long-chain omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil have a wide range of biological activities, including modulating directly and indirectly modulated inflammatory responses and modulating and decreasing cytokine release.
The researchers said that more studies are needed on the relationship between “omega-3” fatty acids and “Covid-19”.
According to the Office of Dietary Supplements ODS , DHA and EPA are found in fish, fish oils and krill oils, but they were originally made by microalgae, not by fish. And when fish consume phytoplankton that consume microalgae, omega-3s build up in their tissues.
After ingestion, dietary fats are degraded in the intestinal lumen and then absorbed. Once in the bloodstream, the lipoprotein molecules diffuse into the body, delivering fats to various organs for subsequent oxidation, metabolism, or storage in adipose tissue.
Omega-3 plays important roles in the body as phospholipid components that form the structures of cell membranes, especially in the retina, brain and sperm.
According to the Office of Dietary Supplements, the adequate intake (Adequate Intakes AIs) of “omega-3” per day for those over the age of 14 years, for males is 1.6 grams, and for females is 1.1 grams, for pregnant women it is 1.4 grams per day, and for nursing mothers 1.3 grams per day.
The content of “omega-3” in fish varies greatly, as fatty fish in cold water, such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, herring and sardines, contain high amounts of “omega-3”, while low-fat fish – such as seabass, tilapia and cod – contain a lower percentage. .
The omega-3 content in fish also depends on the composition of the food the fish consumes. Farmed fish usually contain higher levels of EPA and DHA than wild-caught fish, but it depends on the food they are fed on.
The following is the content of a group of foods of “omega-3” acids in grams (eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid).
Salmon, Atlantic, farmed, cooked, 3 ounces (one ounce equals 28 grams):
Docosahexaenoic acid: 1.24
Eicosapentaenoic acid: 0.59
Salmon, Atlantic, wild, cooked, 3 ounces:
Docosahexaenoic acid: 1.22
Eicosapentaenoic acid: 0.35
Herring, Atlantic, cooked, 3 ounces
Docosahexaenoic acid: 0.94
Eicosapentaenoic acid: 0.77
Sardines, canned in tomato sauce, drained, 3 oz
Docosahexaenoic acid: 0.74
Eicosapentaenoic acid: 0.45
Atlantic mackerel, cooked, 3 oz
Docosahexaenoic acid: 0.59
EPA: 0.43
Salmon, pink, canned, drained, 3 ounces
Docosahexaenoic acid: 0.63
Eicosapentaenoic acid: 0.28
Trout, rainbow, wild, cooked, 3 ounces
Docosahexaenoic acid: 0.44
Eicosapentaenoic acid: 0.40
Shrimp, cooked, 3 ounces
Docosahexaenoic acid: 0.12
Eicosapentaenoic acid: 0.12
Light Tuna, canned in water, drained, 3 ounces
Docosahexaenoic acid: 0.17
Eicosapentaenoic acid: 0.02