Hormones are of great importance in the human body, and their deficiency leads to serious pathological repercussions, and
Hormones are chemicals secreted by the endocrine glands, and poured into the bloodstream directly to reach other organs and tissues for action.
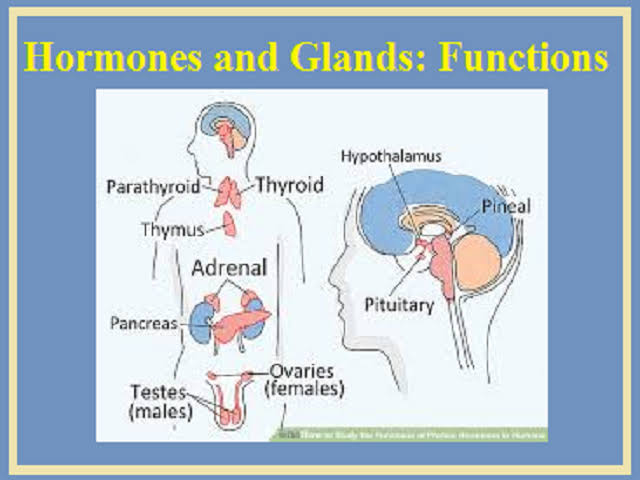
Endocrine
Adrenal
Suprarenal gland
Parathyroid
Thyroid gland
Pituitary gland
placenta
Placenta testis
Testis ovary
Ovary pancreas
Pancreas
types of hormones
Hormones are classified according to their chemical composition into four chemical groups:
Steroids: such as androgens, estrogens.
Derivatives of amino acids: such as thyroxine, adrenaline.
Peptides: such as vasopressin, corticotropin.
Proteins: such as insulin, secretin.
The mechanism of action of hormones
There are three main methods of hormonal activation:
The hormone may activate a gene.
Examples include sex hormones, which have the ability to move into the cell nucleus and bind with nucleic acids (DNA).
The hormone may activate one of the enzymes.
An example is the hormone adrenaline, which activates a specific enzyme inside the cell membrane, and this enzyme causes the desired change while the hormone remains outside the cell membrane.
The hormone may change the ability of the cell wall to allow some substances to pass in or out.
Examples include the hormone insulin and growth hormone, which are two examples of the ability of hormones to change permeability. Insulin allows glucose to enter the cell, while growth hormone allows amino acids to enter the cell for protein synthesis.
Pituitary gland
The pituitary gland is considered the most important gland in the body because it controls other endocrine glands. It is a white gland located at the base of the brain.
The pituitary gland consists of three sections, each of which has its own hormones:
middle lobe posterior lobe anterior lobe
frontal lobe hormones
The anterior lobe hormones contain the following hormones:
Thyroid stimulating hormone. It is a glycoprotein.
Importance: It stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete thyroxine.
Adrenal cortex stimulating hormone. It is a polypeptide chain.
Importance:
Regulates the production and secretion of all adrenal cortex hormones except for aldosterone
It helps to transfer unsaturated fatty acids from adipose tissue to blood plasma.
Increases the process of formation of ketone bodies.
Decreases the rate of formation of urea from amino acids.
Delays the loss of activity of the adrenal cortex hormones in the liver.
Gonadotropin-stimulating hormones.
They are hormones that stimulate and stimulate the gonads. They are of three types:
Follicle-stimulating hormone, which is a glycoprotein.
Importance:
In females, it helps the growth and maturation of the ovarian follicle and prepares it for the secretion of the egg, and stimulates the ovary to secrete beta-estradiol, which is responsible for preparing the uterine wall to receive the egg.
In males, it stimulates the testicles to produce sperm.
The stabilizing hormone is a glycoprotein.
Importance:
In females, it helps to complete the maturation of the egg and the bursting of the follicle and the exit of the egg, and it works on the secretion of estrogens, which is important for the formation of the corpus luteum, which secretes the hormone progesterone important for the continuation of pregnancy.
In males, it activates the secretion of testosterone in the testicles, which is responsible for the libido and the emergence of secondary sex characteristics in males.
Milk secretion hormone, which is a protein.
Importance:
In females, it stimulates the secretion of milk from the mammary glands after birth, and the corpus luteum stimulates the secretion of estrogen and progesterone.
When males do not know his function.
Growth hormone
It is a polypeptide chain.
Its importance: the absence of the hormone in immature animals leads to short stature, and its increase leads to an increase in height