Dietary fiber is wrongly named. It is not ballast, but essential for a functioning digestion. It protects against colon cancer and lowers cholesterol levels. You can meet your needs with 5 portions of fruit and vegetables a day and plenty of whole grain products.
What are fibers and where do they come from?
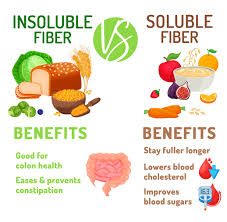
Dietary fiber is a fiber-rich component of plant foods that reaches the large intestine undigested. It consists of long, tasteless sugar chains. There are water-soluble dietary fibers, such as inulin and pectin, which are mainly found in fruit and vegetables. Water-insoluble dietary fibers, such as cellulose and lignin, are mainly found in grains and grain products.
How do they work in the body?
The fiber-rich structures in the mouth mean that food has to be chewed more intensively and for longer. Dietary fiber increases the volume of a meal without adding calories. It ensures that food stays in the stomach for longer, thereby promoting a feeling of fullness. It binds water in the intestines, thereby increasing stool volume. The increased stimulation of the intestinal wall stimulates intestinal movement, thus shortening the time the food remains in the intestines. This means that carcinogenic substances do not have long to come into contact with the intestinal mucosa. This is the basis for the protective effect of dietary fiber against colon cancer.
The increased stool volume due to water improves stool consistency and constipation occurs less frequently. Adequate fluid intake is a prerequisite.
Dietary fiber binds bile acids and flushes the cholesterol they contain out of the body. The body has to produce new bile acids and needs cholesterol to do so, which in turn lowers cholesterol levels.
Scientific studies have shown that meals rich in fiber lead to a reduction in blood sugar levels in diabetics. The reason for this is that fiber delays the absorption of carbohydrates from the intestine into the blood.
Positive colon bacteria require soluble fiber as food and break it down almost completely into short-chain fatty acids. These serve as an energy source for the colon mucosa and maintain the barrier function against harmful germs.
What amount of fiber is recommended?
The German Nutrition Society (DGE) recommends that adults consume 30 g of fiber daily. You can easily achieve this amount by adding five portions of fruit and vegetables/legumes, one portion of cereal flakes, two to three slices of wholemeal bread and one portion of potatoes, wholemeal pasta or brown rice to your diet.
Note: If you have previously eaten a low-fiber diet, you should not change your diet overnight. Your intestines need to get used to the high-fiber diet. To ensure that the fiber has enough water to swell, you need 1.5-2 liters of liquid per day