Our cells are normal activities it produces highly reactive substances that contain oxygen during. Overproduction of these substances into cells and body it can damage their function; it can lead to a condition called “oxidative stress”, which can contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer. Factors that increase the production of free radicals in the body inflammation there may be external factors such as internal or pollution, UV exposure and cigarette smoke.
The Importance of Antioxidant for Our Health
Our body has preventive and restorative mechanisms that regulate oxidative stress pathways. Research has shown that antioxidant enzymes are the most important components of this defense system. Antioxidants can prevent or slow cell damage caused by free radicals; therefore, they are thought to help improve overall health.
Studies have linked oxidative stress to heart disease, cancer, arthritis, stroke, respiratory diseases, immune deficiency, Parkinson’s disease, and other inflammatory or ischemic conditions. Antioxidant intake is believed to reduce these risks.
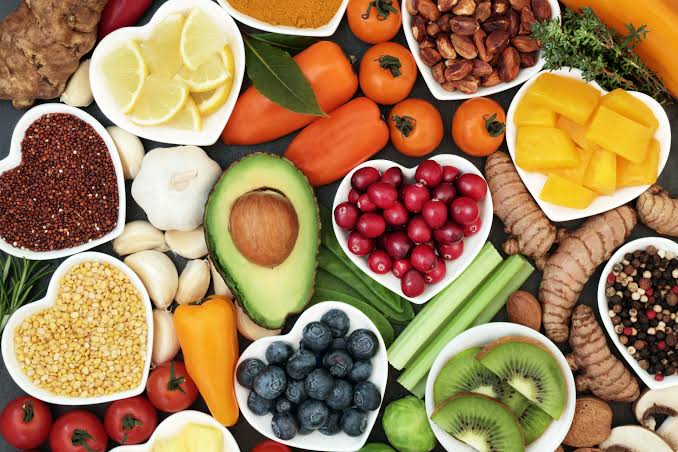
Foods That Contain Antioxidants
Our body produces some antioxidants that we need. In addition, antioxidants can be obtained from foods such as fruits, vegetables and grains. Foods that are especially high in antioxidants are often called “super food” or “functional food”. Some antioxidants, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta-carotene, are also available as dietary supplements.
Antioxidant Capacity
Antioxidant capacity is a measure of a specific free radical that is cleared by a test solution. The measure of antioxidant capacity takes into account the effect of all antioxidants present in plasma and body fluids. Measuring plasma antioxidant capacity can help in assessing physiological, environmental and nutritional factors in humans.