Gastroenterology specialist Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mustafa Kaplan gave information about liver enlargement and its symptoms.
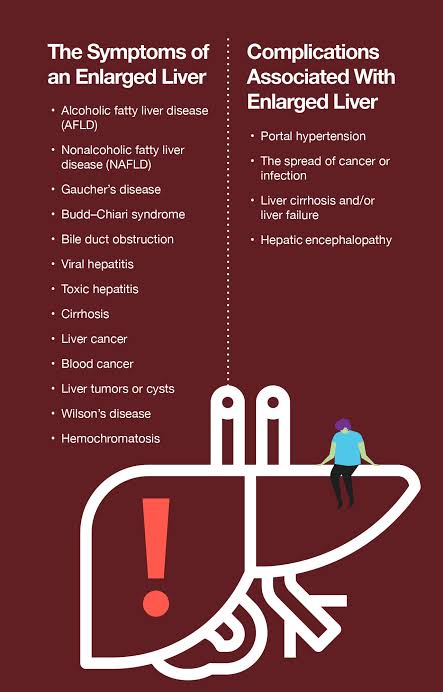
Sometimes the liver can swell as a response to a short-term (acute) condition and then return to normal size on its own after a while. However, a process that begins due to another cause can cause slow but progressive damage to the liver. Early diagnosis is extremely important in liver problems. If it is delayed, liver cirrhosis and liver cancer can develop and liver transplantation may be necessary for treatment.
Patients who generally encounter this problem do not realize that their liver is enlarged for a while. After a while, a feeling of bloating or fullness in the abdomen and pain in the upper right abdomen are noticed. Specialist doctors notice liver enlargement during physical examination.
5 signs of disease-related growth
If liver enlargement is due to a disease, there may be other common symptoms.
Feeling tired
Nausea or loss of appetite
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Dark urine and light-colored stools
Itching on the skin
Liver enlargement can cause these diseases
The liver may become enlarged as a response to hepatitis, infection, or drug injury.
If there is excessive fat storage in the liver (hepatosteatosis, i.e. fatty liver), there will be enlargement.
If the vessels passing through the liver are blocked, the liver becomes enlarged.
If there is alcohol-related hepatitis and associated cirrhosis, the liver may become enlarged.
Toxic hepatitis, usually due to drug overdose
Viral hepatitis due to infection with hepatitis A, B, or C.
Fatty liver disease due to alcohol or metabolic syndrome.
Mononucleosis, a common viral infection.
Hemochromatosis, which causes iron accumulation in the liver, and copper accumulation
Liver enlargement due to genetic diseases such as Wilson’s disease.
A rare disease that causes fat accumulation in the liver: Gaucher disease.
Since the liver is a frequent destination for blood vessels coming from other organs, cancers of organs such as the stomach, pancreas and colon can spread to the liver and enlarge it.
Liver cysts are usually benign, but sometimes animals such as cats and dogs can cause this problem.
Benign liver tumors (hemangioma or adenoma).
Liver cancers.
Systemic cancers, that is, cancers from other organs that spread to the liver.
Blood cancers such as leukemia and lymphoma enlarge the liver and spleen.
Bile duct diseases and strictures.
Heart failure.
Budd-Chiari syndrome, which is a blockage in the veins coming out of the liver.