minerals in the human body
The human body needs a lot of minerals. Despite its presence in very small quantities, the human body needs it in the formation of bones and blood, in addition to its role in maintaining the normal functions of cells, and minerals work side by side with vitamins to form enzymes necessary for vital processes in the human body, so if the enzyme lacks any of The metallic elements become inactive and unable to function properly.
Minerals are classified into two categories: major minerals, which are the minerals that the body needs in large quantities (more than 100 mg per day), such as: calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, chlorine, and magnesium. secondary minerals; They are the elements that the body needs in very small quantities, such as: zinc, iron, manganese, iodine, fluorine, selenium, and chromium.
Potassium element and its importance to the body
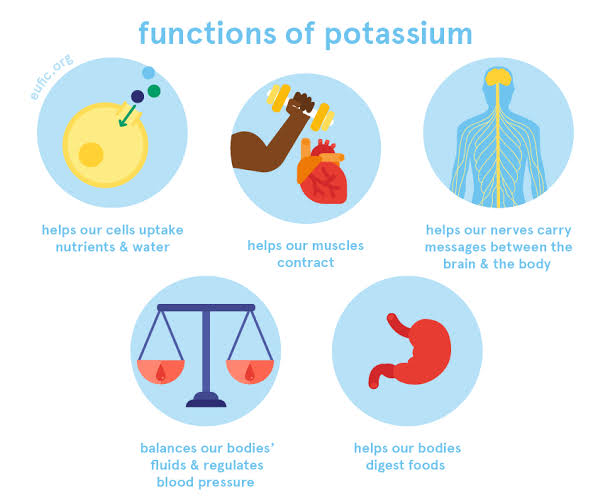
Potassium (k) is one of the main minerals in the human body, and its importance lies in the following:
Transmission of nerve impulses by exchanging sodium and potassium ions across the cellular membranes of nerves.
• lowering blood sugar; Diabetics are advised to be careful to eat foods rich in potassium in a certain proportion.
• Potassium helps prevent muscle spasms; Muscle spasm is a symptom of potassium deficiency in the blood, as potassium helps relax muscles and reduce spasm.
• Preserving bone health, increasing its density, and preventing osteoporosis, by maintaining the balance of acids necessary to preserve calcium within the body.
• improve brain function; Where potassium maintains brain electricity, it is also very effective in learning and maintaining a strong memory, in addition to helping to carry oxygen to the brain.
• Maintaining the acid-base balance in the bloodstream.
• maintaining normal blood pressure; it reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease.
• Improving the metabolism process, by facilitating the digestion of both fats and carbohydrates, as it is an important component in the formation of proteins.
• reduce anxiety and stress; Eating foods rich in potassium has a significant impact on relieving chronic anxiety that some people may experience as a result of different life circumstances.
• Maintaining the moisture of skin cells.
Natural sources of potassium
The amount of potassium in natural food ranges between 2000 mg to 4000 mg per day, and potassium is abundant in many foods such as: avocados, bananas, lentils, potatoes, sweet potatoes, apricots, melons, dates, kiwi, mangoes, figs, artichokes, and peas. , carrots, milk, yogurt, as well as red meat, fish meat, and it is worth mentioning that the excess amount of potassium is excreted through the kidneys, so people who suffer from kidney problems should reduce their potassium intake to less than 2000 milligrams per day.
potassium deficiency
Due to the presence of potassium as an essential element in the blood, its deficiency may cause an imbalance in the functions of the various body systems, especially the nervous system, and it may pose a threat to the patient’s life. .
Symptoms of potassium deficiency
Symptoms of potassium deficiency include:
• severe weakness in the body.
• The occurrence of muscle spasms.
Constipation.
• The occurrence of heart problems.
skin problems.
• Psychological anxiety and nervous tension.
Weakness in memory, and the patient may suffer from temporary amnesia.
sleep disturbances.
Ringing in the ear.
• Anorexia.
Causes of potassium deficiency
The most common causes of potassium deficiency are:
Medicines such as antibiotics.
Chronic diarrhea.
• Addiction to alcoholic beverages.
Excessive sweating.
Folic acid deficiency.
Following a harsh and unhealthy diet.
Treatment of potassium deficiency
Potassium deficiency is treated in simple cases by using medicines and nutritional supplements, or by eating vegetables that contain potassium, but if the deficiency is significant, treatment is done in the hospital by taking potassium needles intravenously in small proportions because a rapid increase in potassium leads to heart disorders, and thus the possibility of a heart attack, and this may lead to death directly.
increased potassium;
An increase in potassium in the body is not a major problem for healthy people, but it may be a major problem for people who suffer from kidney failure, which leads to a disruption of the role of the kidney in excreting potassium, which increases its concentration. in the blood, and an increase in potassium is detected in the body (in English: Hyperkalemia) by doing a routine blood test.
Symptoms of excess potassium
Symptoms that people with high potassium may complain of include:
Weakness in the muscles.
Numbness and numbness in the extremes.
nausea.
• Heart palpitations.
• Inability to breathe.
Causes of excess potassium
Common causes of excess potassium are:
• Kidney diseases: the kidney balances the amount of potassium taken from the blood with the amount lost in the urine, and healthy kidneys can compensate for the excess potassium in the blood by removing more of it, but if the kidney function is disrupted, it will not be able to remove enough potassium which leads to an increase in blood levels.
• Excessive intake of foods that contain potassium.
• Taking medications that prevent the kidneys from losing enough potassium, which leads to an increase in its level in the blood.
Potassium excess treatment
Increased potassium must be treated urgently through intravenous calcium nutrition to preserve the heart muscle and other muscles from the effect of the increase, and the diet must be changed by eating foods that contain low levels of potassium, and taking diuretics that produce potassium with urine, and it is possible to resort to dialysis. The kidneys remove potassium from the body.