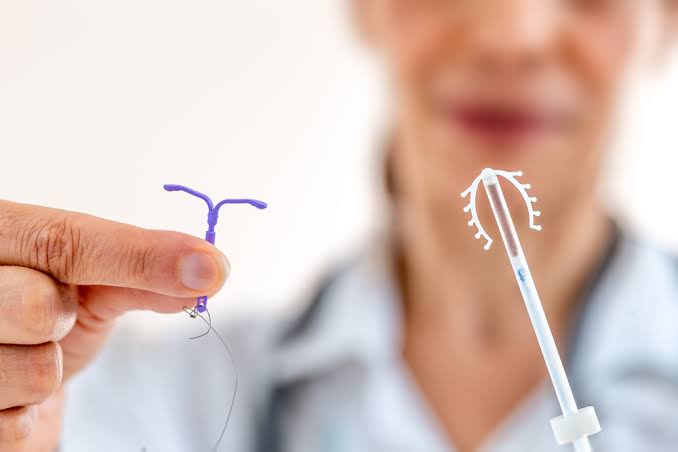
The IUD is a small plastic T-shaped device that is coated with copper or contains some hormones to enable a woman to prevent pregnancy . The IUD is in place by feeling for this string. This string is also used by the doctor to remove the IUD.
Types of spirals:
1. The hormonal IUD:
The hormonal IUD is a form of the hormone progestin, and is considered less effective in preventing pregnancy than the copper IUD. There are two types of hormonal IUDs, one that works for 5 years, and the other works for 3 years.
2. Copper IUD:
This type is the most common, and is a copper wire T-shaped, and the copper IUD can stay in place for up to 10 years, and is very effective for preventing pregnancy.
How does the coil work:
Both types of IUDs prevent fertilization of an egg by damaging or killing sperm, and the IUD also affects the lining of the uterus and prevents a fertilized egg from implanting and growing in the uterine wall .
1. A hormonal IUD prevents fertilization by damaging or killing sperm, and making cervical mucus thick and sticky, so sperm cannot get into the uterus. It also keeps the lining of the uterus from growing, making it unprepared to receive a fertilized egg, and the hormones in this IUD reduce menstrual bleeding and cramping. Read about contraception
2. The copper IUD contains copper , which is toxic to sperm, and this causes the uterus and fallopian tubes to produce a fluid that kills sperm, and this fluid contains white blood cells, copper ions, enzymes, and prostaglandins.
Inserting and using the coil:
The IUD can be inserted at any time, as long as you are not pregnant and do not have any pelvic infections. The IUD is inserted into the uterus by the doctor, and this procedure takes only a few minutes, and it can be done in the doctor’s office, and sometimes a local anesthetic is injected into the uterus. The area around the cervix, but it is not always needed. Inserting an IUD is easier in women who have had a natural delivery in the past.
What to expect after inserting the coil:
After inserting the coil, a woman may experience some cramps and light bleeding for at least a day or two.
Avoid having sex, using tampons, or putting anything in the vagina for the first 24 hours after inserting the IUD.
Follow-up :
- Your doctor may want to see you every 4-6 weeks after the IUD is inserted, to make sure it is still in place.
- Undoubtedly you have to check for the presence of the IUD string after each period, and to do this you have to insert the finger into the vagina and feel the cervix, which is at the top of the vagina, which is a very thin plastic string coming out of the opening of the cervix, and you should consult a doctor on Immediately if you do not feel this chain.
- If you can’t feel the string, it doesn’t necessarily mean that the IUD has been expelled, but sometimes the string is hard to feel, and the ultrasound shows whether the IUD is still there.
- If you suffer from any problems, you should check the existence of the chain after each period and visit the doctor once a year for the necessary examinations.
The coil may be the most appropriate method of birth control in the following cases:
- If you do not have any pelvic infection at the time the IUD is inserted.
- If you and your husband do not carry any diseases or infections that may be transmitted to the other party for those who want an effective and long-acting method of birth control, which requires little effort and is not easily reversible.
- For women who cannot or do not want to use birth control pills.
- A woman who is breastfeeding.
- The copper IUD is recommended for emergency contraception if you have had unsafe sex in the past few days, and you need something to avoid pregnancy. The copper IUD is more expensive than other emergency contraceptives.
How it works:
The IUD is a very effective method of birth control. When using a hormonal or copper IUD, less than one woman out of 100 becomes pregnant in the first 3 years. Most pregnancies that occur with an IUD are due to the IUD being expelled from the uterus unnoticed, and it is likely to come out in the first few months of IUD use. One of the advantages of effective IUDs is that it is low cost, easy to use, reduces the chances of an ectopic pregnancy, and does not cause any problems during intercourse.
Other advantages of the hormonal IUD:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding reduces an average of 90% after the first few months of its use.
- Reduces menstrual bleeding and cramping in postmenopausal women.
- Prevents endometrial cancer.
- Reduces the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- It does not cause weight gain.
Risks of using an IUD include:
Menstrual problems, as the copper IUD may increase menstrual bleeding or cramps, and the hormonal IUD may reduce menstrual cramps and bleeding.
- In 1 in 1000 women, the IUD will cause a perforation or perforation of the uterus, and although it is rare, it may occur during insertion, and if this happens it must be removed immediately.
- Expulsion of the IUD from the uterus may occur in about 2 to 10 out of 100 women during the first year, usually in the first few months of use, and most often when the IUD is inserted immediately after childbirth or in a woman who has never become pregnant.
Disadvantages of the hormonal coil:
A hormonal IUD may cause benign tumors called ovarian cysts, which usually go away on their own. The hormonal IUD can cause hormonal side effects similar to those caused by oral contraceptives, such as breast tenderness, mood swings, headaches, and acne. These side effects usually go away after the first few months.
Pregnancy with an IUD:
If you become pregnant with an IUD, your doctor will recommend that the IUD be removed, because the IUD can cause premature labor or miscarriage (IUDs do not cause birth defects).
Cases that require consulting a doctor immediately:
If you have severe pain in the abdomen or pelvis.
Heavy vaginal bleeding.
Passing blood clots or changing a pad every hour for 2 hours or more.
If you have a vaginal discharge that smells bad, and you have a fever and chills.
If you think you may be pregnant.
An IUD can be a safe method of birth control for women who: Have a
history of ectopic pregnancy, and both copper and hormonal IUDs are suitable.
With a history of menstrual irregularities and pain, a hormonal IUD may be appropriate for those women, women who have a bleeding disorder or those who are taking anticoagulant medications.
Women with diabetes.
Who are you breastfeeding?
The hormonal IUD is a good option for women who have endometriosis