Rotavirus belongs to a family of viruses called Rotaviridae, and there are nine types of it, and it is a circular or circular virus.
According to the World Health Organization, this virus causes the death of between 215 and 250 thousand people annually, due to dehydration caused by diarrhea that occurs as a result of infection, especially among children who did not receive the vaccine against it, which can provide protection for children up to 90 %.
In his article on the Arab Scientific Society Organization’s website, Dr. Reda Muhammad Taha wrote that rotavirus is highly contagious, as it spreads easily among children from three months to 35 months of age, especially in nursing homes, nurseries and schools, where children stay for a long time in those places.
The virus is transmitted through hands contaminated with feces; That is, not washed well, as one gram of infected stool contains more than ten trillion infectious viral particles, while between 10 and 100 particles of rotavirus are sufficient to cause infection.
contaminated food
The virus is also transmitted through contaminated food, especially meals provided on trips and others, as well as through the use of unclean public bathrooms and swimming pools, and the virus may be transmitted from children to adults also in endemic areas, especially in poor countries that lack clean drinking water.
Dr. Taha – an assistant professor of microbiology at the Faculty of Science at Fayoum University – said that the virus is able to survive for long hours and transmit infection through contaminated hands, especially children who constantly put their fingers in their mouths, and the virus remains on the surfaces of things for weeks, retaining its ability to transmit. Infection, if surfaces, utensils or tools contaminated with the virus are not cleaned well with highly effective disinfectants.
The virus encodes the production of a type of toxin inside the intestine, “Enterotoxin”, consisting of a glycoprotein, called “NSP4” for short. This poison causes an imbalance between calcium and sodium; As a result, the body loses fluids in the form of severe diarrhea.
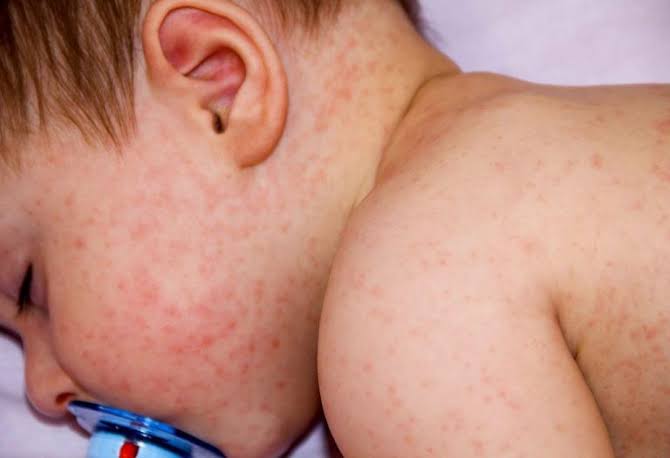
Symptoms of infection with the virus – in addition to severe watery diarrhea – include vomiting, fever and pain in the abdomen, and the virus also causes gastroenteritis, and infection may lead to death if the patient does not undergo the correct treatment.
studies
Symptoms may last for approximately eight days, which calls for rapid treatment first by injecting solutions to prevent the risks of dehydration, and as prescribed by the specialist doctor.
There are many published studies on rotavirus, the way it works, ways to treat it, and the symptoms it causes, especially diarrhea.
A study – conducted by researchers from the Institute of Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State University in Atlanta, United States, and published in the “Cell” journal in October 2019 – describes the mechanism by which an infected person resists the virus, and its results revealed a type of naturally segmented filamentous bacteria Within the person’s microbiome in the gut, it is called “SFB” (SFB), which is the determining factor in the ability of the infected person to resist and get rid of the virus, as these bacteria reduce the destruction of cells caused by the rotavirus, by constantly helping them change the squamous layer. of the intestine in which the virus is present.
This research team is an important step in explaining the mechanism by which these bacteria are able to expel the virus with excreta, and scientists are seeking to simulate this mechanism to find an effective treatment to get rid of this virus.