Can gluten in bread trigger anxiety? Discover the link between gluten, mental health, and whether reducing gluten may ease anxiety symptoms.
The Gluten–Anxiety Connection
Bread, pasta, and baked goods are staples in many diets. But for some people, gluten—a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye—may not just cause digestive discomfort. Recent studies suggest that gluten could also influence mental health, particularly anxiety and mood disorders
How Could Gluten Trigger Anxiety?
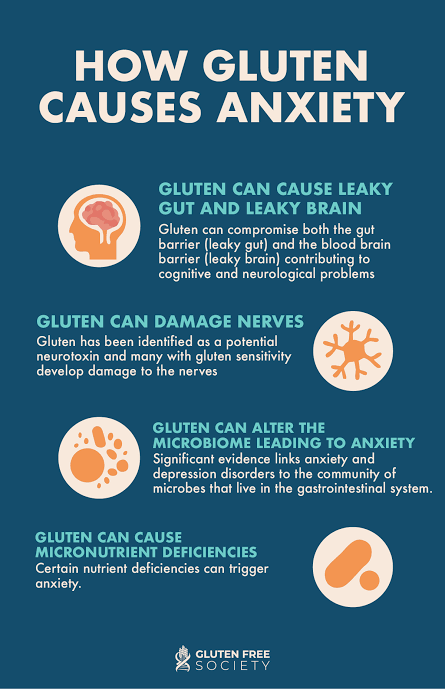
Gut–Brain Axis Disruption
The gut and brain are connected through the vagus nerve and microbiome.
Gluten sensitivity may cause inflammation in the gut, which can affect brain function.
Immune Response
In people with celiac disease, gluten triggers an immune attack that may release inflammatory molecules, linked to anxiety and depression.
Nutrient Absorption Problems
Gluten sensitivity can reduce absorption of vitamins like B12, folate, and iron, which are vital for mental health.
Psychological Stress
Chronic digestive symptoms from gluten intolerance (bloating, pain, diarrhea) can indirectly increase stress and anxiety levels.
Gluten, Anxiety, and Different Groups
Celiac Disease Patients – Often report reduced anxiety after following a strict gluten-free diet.
Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity – Some people experience mood improvements when avoiding gluten, even without celiac disease.
General Population – For most, bread and gluten are not directly linked to anxiety.
Should You Avoid Bread to Reduce Anxiety?
If you suspect gluten sensitivity, consult a doctor before cutting it out.
A balanced diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, omega-3s, and probiotics is essential for mental health.
Going gluten-free unnecessarily may lead to nutritional deficiencies (fiber, B vitamins
Gluten may contribute to anxiety in sensitive individuals, especially those with celiac disease or gluten intolerance. However, for most people, bread is not a direct cause of anxiety. If you notice a link between gluten and your mood, consider professional testing before making dietary changes.